DNS stands for domain name system. A DNS server is a critical part of the computer networks, it is used to get the IP address of a server, with the help of the domain name of that server.
Just like a phone book, gives us the phone number of a person corresponding to that person's name, the DNS server gives us the IP address of a server corresponding to that server's domain name.
How does a DNS server work?
When we click on a link, our device tries to establish a connection with that website, and to do so, it needs the IP address of that website.
So, when we type the URL in the browser's address bar, that URL is sent in the form of a query to your ISP's( internet service provider ) DNS server.
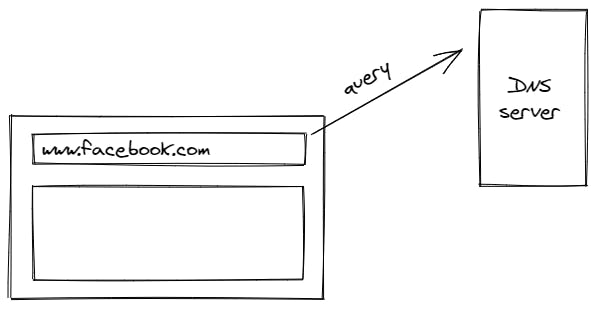
The DNS server then firstly looks for the URL's corresponding IP address in its resolver cache and responds with the IP address if found. The resolver cache stores all the most recently visited websites and their corresponding IP addresses.
Let's just assume that you typed a website that was not present in the resolver cache, then what will happen next?
Next, the DNS server will pass the query to the root servers, and in total there are thirteen root servers and any one of them could give a response back with the IP address of the TLD server.
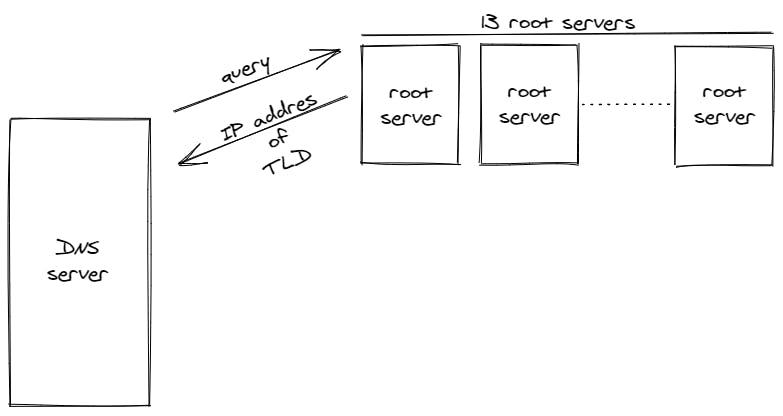
TLD( Top Level Domain ) servers stores the information of all the domains that share a common domain extension,e.g., .com, .in, .net, etc.. ( the part after the last dot in an URL ). Each domain extension has a separate TLD server. For example, a .com TLD server contains information for every website that ends with '.com'.
The query is then sent to the TLD server by the DNS server and the TLD server responds with the IP address of the authoritative server.
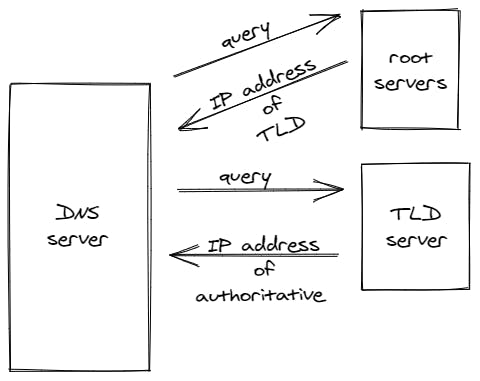
Authoritative servers know all about the URLs, passed by the DNS servers as queries. These servers are the ones that help us to deploy our websites, and they have complete authority over them. Example: route 53 by amazon.
The authoritative servers on receiving the query from the DNS server, respond with the IP address of the URL that was passed with the query.
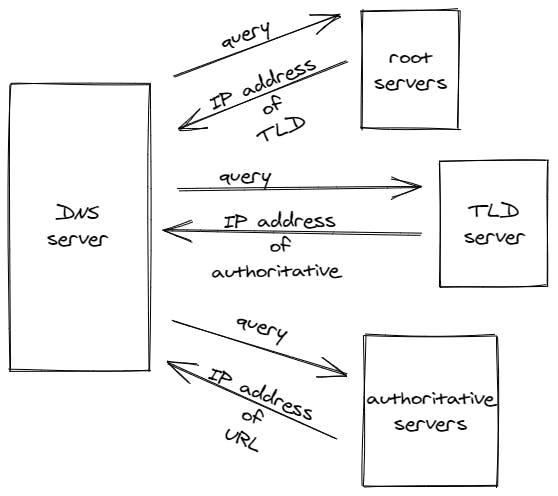
The DNS server upon receiving the IP address from the authoritative servers sends it to the browser, and after that, the URL along with its IP address is stored in the resolver cache and after a certain amount of time, the information is flushed out of the cache. This time period is determined by the TTL( Time To Live ) factor, which is set by the owner of the domain.

